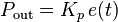- Proportional-integ/ral-derivative controller (PID controller) is a control loop feedback mechanism (controller) widely used in industrial control systems. A PID controller calculates an error value as the difference between a measured process variable and a desired setpoint. The controller attempts to minimize the error by adjusting the process through use of a manipulated variable.
- Three separate constant parameters, and is accordingly sometimes called three-term control the proportional, the integral and derivative values, denoted P, I, and D.
What is a Propotional?
- Produces an output value that is proportional to the current error value. The proportional response can be adjusted by multiplying the error by a constant Kp, called the proportional gain constant.
- The proportional term is given by:
- A high proportional gain results in a large change in the output for a given change in the error.
- If the proportional gain is too high, the system can become unstable (see the section on loop tuning). In contrast, a small gain results in a small output response to a large input error, and a less responsive or less sensitive controller.
- If the proportional gain is too low, the control action may be too small when responding to system disturbances.
- Tuning theory and industrial practice indicate that the proportional term should contribute the bulk of the output change.
What is a Integral ?
- The contribution from the integral term is proportional to both the magnitude of the error and the duration of the error.
- The integral in a PID controller is the sum of the instantaneous error over time and gives the accumulated offset that should have been corrected previously.
- The accumulated error is then multiplied by the integral gain (
 ) and added to the controller output.
) and added to the controller output. - The integral term is given by:

- The integral term accelerates the movement of the process towards setpoint and eliminates the residual steady-state error that occurs with a pure proportional controller.
- The integral term responds to accumulated errors from the past, it can cause the present value to overshoot the setpoint value.


- Boleh mengatasi offset yang didapati dalam kawasan berkadaran.
- Dapat mengawal sekiranya sistem tersebut terdapat perubahan pada beban.
- Hanya sesuai digunakan pada suatu sistem yang mempunyai perubahan yang besar.
What is Derivative ?
The process error is calculated by determining the slope of the error over time and multiplying this rate of change by the derivative gain Kd.
The derivative term is given by:
Derivative action predicts system behavior and thus improves settling time and stability of the system.
An ideal derivative is not causal, so that implementations of PID controllers include an additional low pass filtering for the derivative term, to limit the high frequency gain and noise.
Derivative action is seldom used in practice though by one estimate in only 25% of deployed controllers because of its variable impact on system stability in real-world applications.
The magnitude of the contribution of the derivative term to the overall control action is termed the derivative gain, Kd.
- 1)Hubungan antara keluaran dan ralat adalah linear.
- 2)Nilai julat ralat untuk 0% ke 100% keluaran pengawal dinamakan ruang berkadaran atau propotional.
- Keburukkan kawalan berkadaran.
- 1)Wujudnya offset dalam mencapai kestabilan.
- 2)Offset ini boleh dikurangkan dengan memberikan nilai gandaan yang tinggi.
Kebaikkan pengawal kamilan.
Keburukkan pengawal kamilan
- PI controller will eliminate forced oscillations and steady state error resulting in operation of on-off controller and P controller respectively.
However, introducing integral mode has a negative effect on speed of the response and overall stability of the system.
Thus, PI controller will not increase the speed of response. It can be expected since PI controller does not have means to predict what will happen with the error in near future. This problem can be solved by introducing derivative mode which has ability to predict what will happen with the error in near future and thus to decrease a reaction time of the controller.
PI controllers are very often used in industry, especially when speed of the response is not an issue.
P+I EQUATION
P+D CONTROLLER
In general it can be said that P controller cannot stabilize higher order processes.
For the 1st order processes, meaning the processes with one energy storage, a large increase in gain can be tolerated. Proportional controller can stabilize only 1st order unstable process. Changing controller gain K can change closed loop dynamics. A large controller gain will result in control system with:
a) smaller steady state error, i.e. better reference following
b) faster dynamics, i.e. broader signal frequency band of the closed loop
system and larger sensitivity with respect to measuring noise
c) smaller
P+I+D CONTROLLER
PID controller has all the necessary dynamics: fast reaction on change of the controller input (D mode), increase in control signal to lead error towards zero (I mode) and suitable action inside control error area to eliminate oscillations (P mode).
Derivative mode improves stability of the system and enables increase in gain K and decrease in integral time constant Ti, which increases speed of the controller response.
PID controller is used when dealing with higher order capacitive processes (processes with more than one energy storage) when their dynamic is not similar to the dynamics of an integrator (like in many thermal processes). PID controller is often used in industry, but also in the control of mobile objects (course and trajectory following included) when stability and precise reference following are required. Conventional autopilot is for the most part PID type controllers.
CONCLUSION OF CONTROLLER
the conclusion of our group members can identify the pros and cons of the system in addition to learning the basics of control and recognize what was the basic controls